Stainless Steel Sheets: A Core Material for the Modern World
In today’s advanced world, stainless steel sheets have become one of the most in-demand and strategic steel products. These sheets are renowned not only for their unmatched resistance to corrosion and rust but also for their high heat resistance and attractive, glossy appearance. These qualities make stainless steel an ideal choice for a wide range of industrial, construction, household, and decorative applications.
But where do these extraordinary properties come from? And how do you choose the best type of stainless steel sheet for your project? Below, we will answer all these key questions to help you make an informed decision.

What is Stainless Steel? The Secret to Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel sheet is essentially an alloy steel sheet containing a minimum of 10.5% chromium in its chemical composition. This vital element, chromium, is the primary secret behind stainless steel’s amazing corrosion resistance!
The “Passivation” Phenomenon: The Invisible Shield of Corrosion Resistance When chromium comes into contact with oxygen in the air, it rapidly forms an extremely thin, invisible, and stable layer of chromium oxide on the metal’s surface. This layer, known as the “passive layer,” acts like a protective shield, preventing oxygen from reaching the iron in the steel. This way, the steel is protected from rust and corrosion, bestowing upon it its “stainless” property.
The higher the percentage of chromium in the alloy, the stronger and more stable this passive layer will be, resulting in increased corrosion resistance. In addition to chromium, other crucial alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum significantly contribute to improving mechanical properties, enhancing corrosion resistance in specific environments, and stabilizing the passive layer. This intelligent combination of elements is what makes stainless steel an unrivaled material.




Types of Stainless Steel Sheets: A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Grade for Every Project
Stainless steel sheets are categorized based on their metallurgical structure, alloying elements, and mechanical properties. Selecting the appropriate grade plays a crucial role in the performance and durability of the final product. Here, we will explore the most common and widely used types of stainless steel sheets:
- Austenitic Stainless Steel (300 Series): The Most Versatile and Widely Used
- Characteristics: The austenitic structure of these grades makes them non-magnetic and provides excellent weldability, formability, and corrosion resistance. The 300 series grades are widely used across various applications due to their optimal balance between cost and performance.
- Most Common Grades:
- Stainless Steel 304 (Most Common Grade):
- Chemical Composition: 18% Chromium and 8% Nickel (18/8).
- Features: Excellent general corrosion resistance, superb weldability, and formability. Stainless Steel 304 is an ideal choice for applications requiring good corrosion resistance, ease of fabrication, and reasonable cost.
- Applications: Industrial and domestic kitchen equipment, sinks, food and dairy industries, water tanks, architectural railings and facades, pipes, and fittings.
- Stainless Steel 316 (Superior Resistance to Chlorides and Acidic Environments):
- Chemical Composition: 16% Chromium, 10% Nickel, and 2% Molybdenum.
- Features: The addition of molybdenum significantly enhances its resistance to specific types of corrosion, especially by chlorides (such as seawater and road salts) and strong acidic environments. Stainless Steel 316 also offers improved resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
- Applications: Chemical and petrochemical industries, marine and coastal equipment, pharmaceutical and medical industries, water treatment equipment, tanks, and pipes containing corrosive chemicals.
- Note: The price of Stainless Steel 316 is typically higher than Stainless Steel 304 due to the presence of molybdenum.
2.Stainless Steel 310 & 309 (Heat-Resistant Grades):
-
-
- Chemical Composition: High percentages of Chromium and Nickel.
- Features: Exceptional resistance to very high temperatures and oxidation at temperatures up to approximately 1100°C.
- Applications: Industrial furnaces, heat exchangers, refinery equipment, cement kiln parts, industrial ovens, and any application exposed to extremely high temperatures.
2. Ferritic Stainless Steel (400 Series): Economical, Magnetic, and Versatile
- Characteristics: These grades primarily contain chromium (ranging from 11% to 30%) and are either nickel-free or contain very low amounts of nickel. Their metallurgical structure, known as ferrite, makes them magnetic. Their corrosion resistance is generally lower compared to austenitic grades (such as 304 and 316), especially in chloride-containing and strong acidic environments. However, they demonstrate good resistance to atmospheric corrosion and Stress Corrosion Cracking. Key advantages of ferritic grades include their lower cost (due to the absence of expensive nickel), suitable weldability in some grades, and good heat resistance. Additionally, their coefficient of thermal expansion is similar to carbon steel, which is an advantage in certain specific applications. Their cold workability is less than that of austenitics, and greater caution is required when welding thicker sections.
- Most Common Grade:
- Stainless Steel 430 Sheet:
- Chemical Composition: Approximately 17% Chromium and nickel-free.
- Features: This is the most widely used type of ferritic stainless steel. It offers good resistance to atmospheric corrosion and mild acids, and provides suitable polishability.
- Applications: Due to its cost-effectiveness and attractive appearance, it is used in the manufacturing of household appliances (such as refrigerators and washing machines), economical sinks, automotive trim, interior and exterior building panels,
3.Martensitic Stainless Steel (400 Series): Hard, Durable, and Heat-Treatable
- Characteristics: These grades typically contain chromium (ranging from 11% to 17%) and a small amount of carbon, and they are nickel-free. Their martensitic structure is achieved after heat treatment (quenching and tempering), which imbues them with exceptionally high hardness and strength. While their corrosion resistance is lower compared to austenitic grades, they are ideal for environments demanding high hardness and wear resistance alongside moderate corrosion resistance. These grades are magnetic.
- Applications: Owing to their superior hardness and wear resistance, martensitic stainless steels are extensively utilized in the manufacturing of high-quality blades and knives, surgical instruments, springs, bearings, shafts, pumps, and valve components that require robust strength and hardness.
Regarding the most common grade:
However, widely used and well-known martensitic grades include:
- Stainless Steel 410: Often considered a general-purpose martensitic grade, offering a good balance of strength and corrosion resistance for mild environments.
- Stainless Steel 420: Known for its higher carbon content, leading to greater hardness and strength (e.g., for cutlery and surgical instruments)

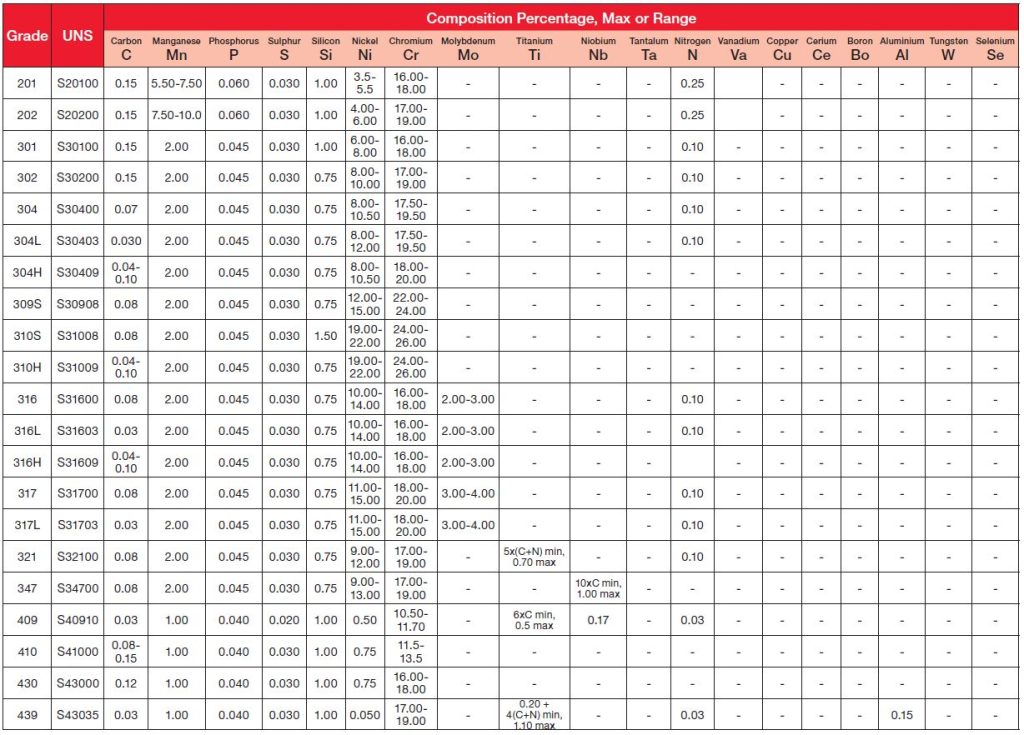
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Sheet: Your Key to Project Success
Selecting the correct stainless steel sheet is crucial for the success of your projects. This guide will help you make the best choice in the shortest possible time.
Sheet Thickness:
- Thin (0.3 to 1 mm): Ideal for high flexibility (packaging, medical, household appliances).
- Medium (1.2 to 3 mm): Suited for strength and weldability (kitchenware, food processing, construction).
- Thick (3 to 6 mm): Designed for pressure resistance (oil, gas, petrochemical, construction).
- Very Thick (6+ mm): For exceptional structural integrity (heavy industries, military, bridge construction).
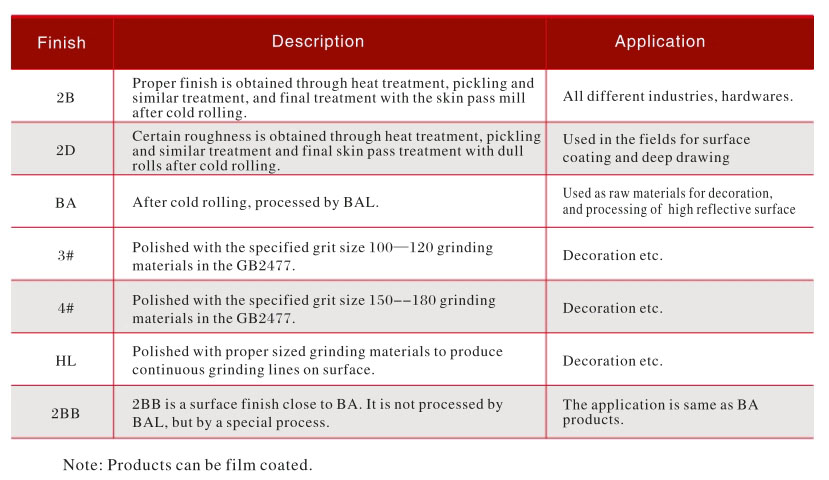
Stainless Steel Surface Finishes:
- Matte:
- 2B: Smooth and economical (kitchen equipment, food processing industries).
- 2D: Rough for paint adhesion (heavy industries).
- Brushed:
- No.4: Fine, modern lines (facades, decoration, elevators).
- Bright:
- BA: Smooth and corrosion-resistant (medical, food, laboratory equipment).
- No.8: Mirror-like and luxurious (facades, decoration).
- Patterned/Embossed: Textured and anti-slip (flooring, wall cladding, elevators).
- Colored: Achieved via PVD or powder coating for diverse aesthetics (facades, decoration, automotive).
Key Selection Tip:
- Corrosive Environment: Bright finish
- Hygiene-Critical: Bright or Matte finish
- Aesthetics: Brushed, Mirror, or Patterned
- Cost Efficiency: Matte < Brushed < Bright/Patterned
Extensive Applications of Stainless Steel Sheets Across Various Industries
Due to its unique properties, stainless steel sheets are widely applied in numerous industries:
- Food & Beverage Industry: Tanks, production lines, cooking equipment, and packaging (hygienic applications).
- Pharmaceutical & Medical Industry: Laboratory equipment, surgical instruments, clean work surfaces.
- Chemical & Petrochemical Industries: Tanks, pipes, reactors, and heat exchangers (resistant to corrosive chemicals).
- Construction & Architecture: Facades, interior decoration, railings, roofs, elevators, and urban furniture (aesthetics and durability).
- Household Appliances: Sinks, washing machines, refrigerators, ovens, and microwaves.
- Automotive Industry: Exhaust components, interior trim, and parts of the vehicle body.
- Marine Industry: Ship components, coastal structures, and underwater equipment (resistant to saltwater).
- Oil & Gas Industry: Refinery equipment, pipelines in corrosive environments, and cooling

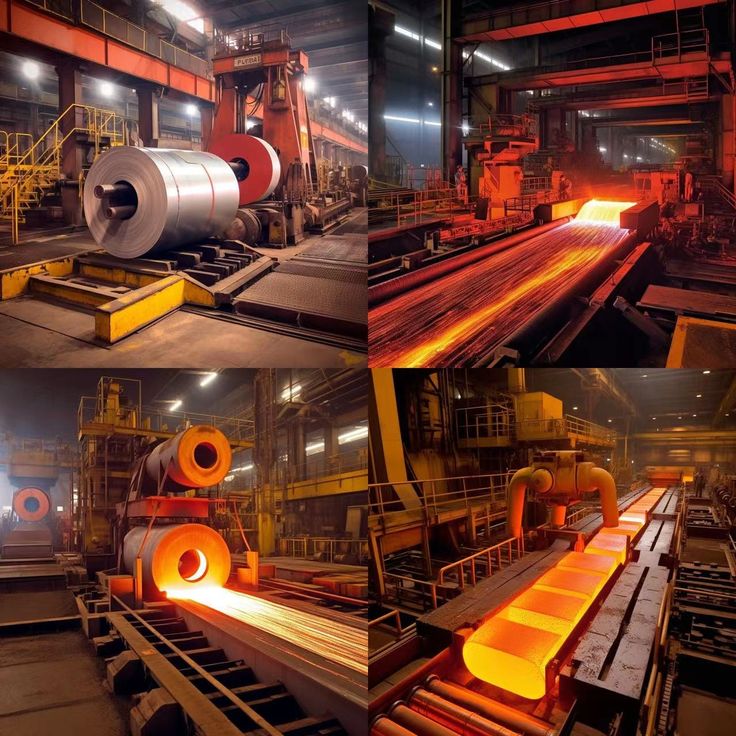
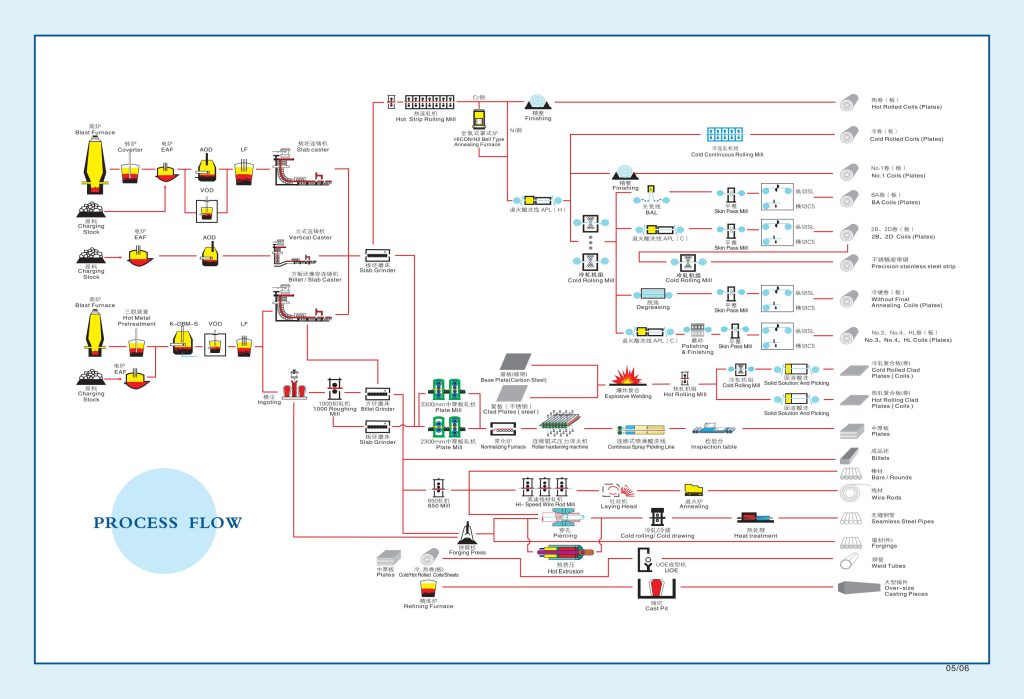
Stainless Steel Sheet Production Process: From Furnace to Final Finish
The manufacturing of stainless steel sheets is a precise and multi-stage process:
- Melting and Alloying: In this initial stage, raw materials such as steel scrap, ferrochrome, ferronickel, and ferromolybdenum are melted in high-temperature furnaces. Various elements are then meticulously added to this molten mixture to create an alloy with the desired characteristics.
- Primary Shaping (Casting): The molten steel is poured into molds to form slabs or ingots. These pieces serve as the raw material for the subsequent stages of stainless steel sheet production.
- Hot Rolling (Conversion to Sheet): Hot slabs pass through large, heavy rollers and, under immense pressure, are gradually thinned and widened to form stainless steel sheets of standard thicknesses.
- Cold Rolling (If Required): For the production of thinner stainless steel sheets with more precise dimensions and a smoother surface, a cold rolling process is employed. This stage significantly enhances the sheet’s precision and surface quality.
- Property Improvement (Annealing): The produced stainless steel sheets undergo an annealing process, which is a form of heat treatment. This improves the sheet’s mechanical properties, such as ductility and strength, and reduces the hardness resulting from the rolling process.
- Cleaning and Finishing (Final Finish): In this stage, any oxide layers that may have formed on the sheet’s surface are removed through pickling (acid washing). Subsequently, the sheet’s surface is polished and prepared according to desired standards. These finishes can include various types such as 2B, BA, No.4, HL, and No.8, each with its unique aesthetic characteristics and applications.
Stainless Steel Sheet Pricing & Purchase: Key Determining Factors
The price of stainless steel sheets is influenced by several factors that are essential for making a smart purchase:
- Steel Grade: Stainless Steel 316 (due to molybdenum) is typically priced higher than 304. Heat-resistant and special grades are more expensive.
- Thickness and Dimensions: Thicker and larger sheets generally incur higher costs.
- Surface Quality (Finish): Special finishes such as mirror (No.8) or polished finishes increase the price.
- Manufacturer and Brand: Reputable global and domestic brands often command premium pricing.
- Global Market Fluctuations: Prices are affected by global nickel, chromium prices, and exchange rates.
- Supply and Demand: The balance of supply and demand in the market.
To receive expert consultation on selecting the appropriate stainless steel grade and dimensions, inquire about the daily price of stainless steel sheets, and ensure the purchase of high-quality stainless steel for your projects, please contact our experienced specialists. We are ready to provide the best solutions tailored to your specific needs.
















