Stainless Steel Pipe
Stainless steel pipe, which is essentially a specific type of steel pipe, is produced by adding elements such as chromium and nickel to the steel alloy. This chemical composition leads to the formation of a passive chromium oxide layer on the pipe’s surface, making it highly resistant to rust, corrosion, and oxidation. This characteristic makes stainless steel pipes ideal for corrosive
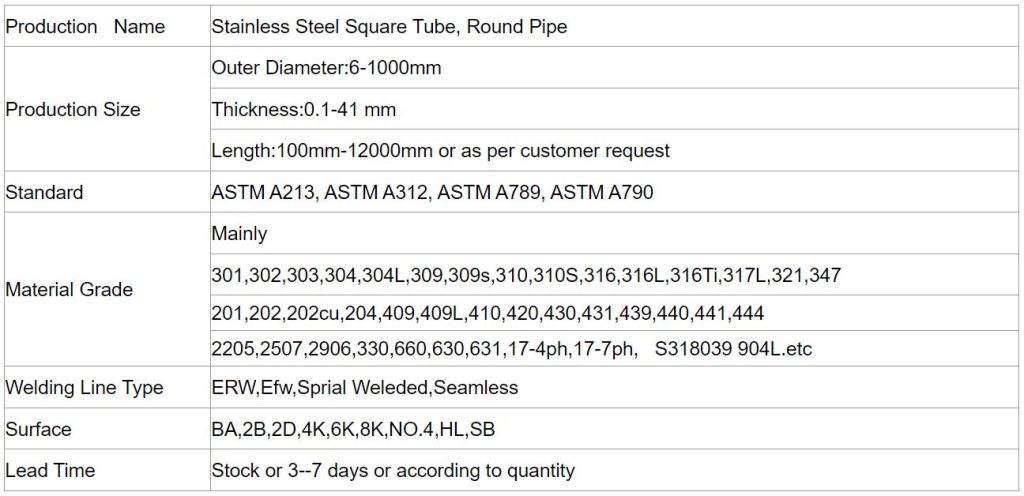
Common Types of Stainless Steel Pipes and Their Characteristics:
Stainless steel pipes are produced in a variety of grades, each optimized with a unique chemical composition and mechanical properties for specific environments and applications. Choosing the correct grade ensures optimal performance and a long lifespan for your system.
Stainless Steel 304 Pipe (Most Common in General Applications):
-
- Characteristics: This is the most widely used type of austenitic stainless steel. Due to its good resistance to general corrosion and excellent weldability and formability, it is the primary choice for many piping systems. SS 304 pipe is available in both seamless (Manisman) and welded forms.
- Applications: Ideal for water transmission lines, food and beverage industries, pharmaceuticals, pumping equipment, and general industrial piping requiring moderate corrosion resistance and ease of installation. (For more details on the general properties of this grade, please refer to the “Stainless Steel Sheet” section).
- Stainless Steel 316 Pipe (Resistant in Corrosive and Marine Environments):
- Characteristics: Due to the addition of molybdenum, this grade offers exceptional resistance to localized corrosion (especially against chlorides and acids). SS 316 pipe is also available in both seamless and welded forms and is preferred for highly corrosive environments or slightly higher temperatures than 304.
- Applications: Essential for chemical industries, petrochemicals, marine and shipbuilding, refineries, and saltwater treatment systems exposed to aggressive fluids. (For more details on the general properties of this grade, please refer to the “Stainless Steel Sheet” section).
- Stainless Steel 321 Pipe (High Temperature Resistance and Welding Applications):
- Characteristics: This grade contains titanium, which enhances its resistance to intergranular corrosion after welding and its performance at high temperatures (up to approximately 900°C). This feature makes it ideal for thermal applications and frequent welding.
- Applications: Suitable for exhaust systems, boilers, heat exchangers, and any application requiring stability in high operating temperatures.
- Heat-Resistant Pipes (e.g., Grades 309 and 310): Stability in Extreme Heat:
- Characteristics: These pipes are designed with high percentages of chromium and nickel, providing exceptional resistance to oxidation and creep at very high temperatures (up to approximately 1100°C for 310).
- Applications: Essential for manufacturing components of industrial furnaces, very high-temperature heat exchangers, and process equipment exposed to severe and prolonged heat
Choosing the Right Pipe: Steel Pipe or Stainless Steel Pipe?
The decision between using a steel pipe and a stainless steel pipe depends on various factors:
- Operating Environment: If the pipe will be exposed to moisture, corrosive chemicals, or salts, stainless steel pipe is the superior choice due to its unparalleled corrosion resistance. For drier environments or structural applications, steel pipes are more suitable.
- Pressure and Temperature: Both types can withstand high pressure and temperature. However, for extremely high pressures, seamless steel pipe (Manisman) performs more specialized, and for very high temperatures, specialized heat-resistant stainless steel pipes are ideal.
- Budget: The price of steel pipe (especially welded) is typically lower than stainless steel pipe. If corrosion resistance is not a critical factor, steel can be a more economical option.
- Hygiene Requirements: In the food and pharmaceutical industries, hygienic stainless steel pipes (with smooth surfaces and corrosion resistance) are mandatory.
Steel Pipe Manufacturing Methods: Hot Rolling and Cold Rolling
Steel pipes and stainless steel pipes, although differing in alloy details and final application, share two main production methods in terms of shaping processes: Hot Rolling and Cold Rolling. Each of these methods offers distinct characteristics and advantages, which we will explore below.
Hot Rolling: Production of Strong, High-Volume Pipes
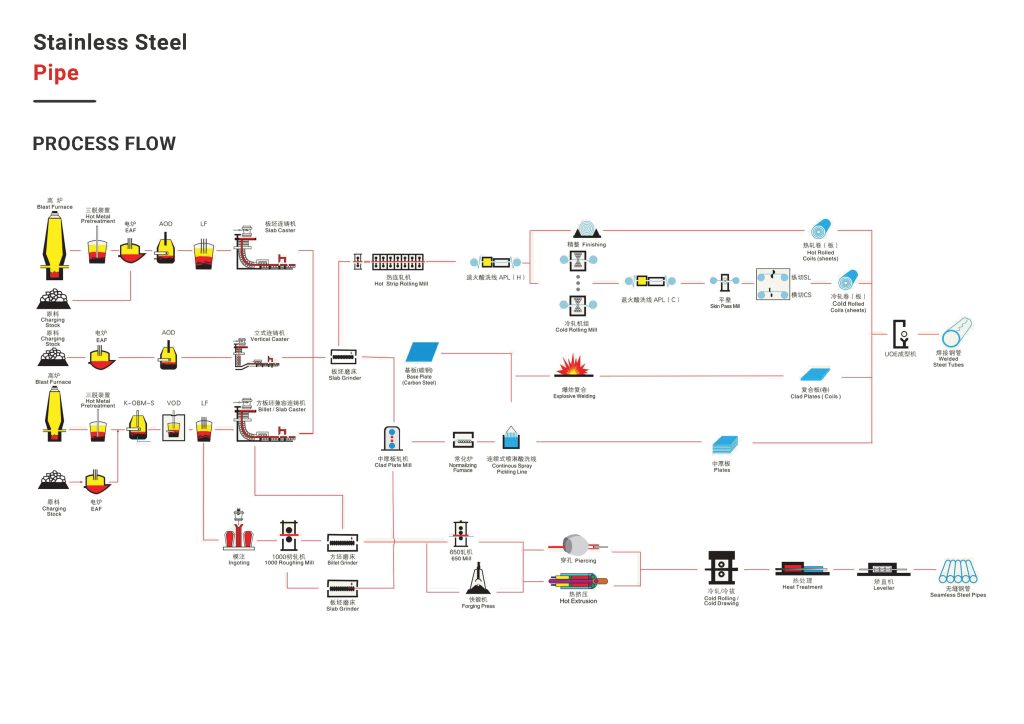
Hot rolling is a process where steel billets or slabs are heated to a temperature significantly above the steel’s recrystallization point (typically above 1100°C). This high temperature increases the metal’s ductility and reduces its hardness, making it easier to shape.
Hot Rolling: Fast and Cost-Effective Shaping
Hot rolling is a process performed at high temperatures (above the steel’s recrystallization temperature). This process allows for easier and faster shaping of the metal.
- Main Stages of Pipe Production with Hot Rolling:
- Billet Preparation: Selecting suitable steel billets.
- Pre-heating: Heating billets to the required temperature in special furnaces.
- Descaling: Removing the oxide layer (scale) from the metal surface.
- Rolling Operation: Passing the heated billet through rollers to reduce thickness and transform it into a pipe. In seamless pipe production, a mandrel is used to create the internal bore.
- Cooling and Cutting: Gradually cooling and cutting the pipes to desired lengths.
- Finishing Operations: Inspection, mechanical testing, chamfering edges, and packaging.
- Advantages of Hot Rolling:
- High Formability: Enables large deformations due to high temperatures.
- Increased Production Rate: Faster process suitable for mass production.
- Reduced Internal Stresses: The metal releases its stresses during cooling.
- Cost-Effective: Generally has a lower production cost.
- Suitable for Thick and Large Sections: Ideal for gas pipes, large-diameter industrial pipes, and sections that do not require high dimensional precision.
Cold Rolling: High Precision and Superior Surface Quality
Cold rolling is performed at room temperature or slightly higher and is typically applied to pipes that have already been hot-rolled. The goal of this process is to improve dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and mechanical properties.
- Main Stages of Pipe Production with Cold Rolling:
- Raw Material Preparation: Surface cleaning and pickling of initial pipes.
- Rolling: Passing the pipe through precise rollers to reduce wall thickness and diameter, and increase length.
- Washing and Annealing: Electrolytic washing and annealing heat treatment to reduce hardness and increase ductility.
- Surface Finishing and Final Inspection: Surface treatment and meticulous dimensional and quality inspection.
- Advantages of Cold Rolling:
- Very High Dimensional Accuracy: Produces pipes with extremely tight tolerances.
- Excellent Surface Quality: Smooth, bright, and scale-free surface.
- Improved Mechanical Properties: Increased tensile strength and hardness.
- Suitable for Thin and Precise Sections: Ideal for furniture pipes, precision stainless steel pipes, and pipes for hygienic and decorative applications.
- Application in Sensitive Industries: Such as automotive, household appliances, and medical equipment.
Key Differences Between Hot and Cold Rolling in Pipe Production:
| Feature |
Hot Rolling |
Cold Rolling |
| Process Temperature |
Above recrystallization (approx. 1100+°C) |
Room temperature or slightly higher (below recrystallization) |
| Dimensional Accuracy |
Less precise, wider tolerances |
Very precise, tighter tolerances |
| Surface Quality |
Rougher, with oxide scale (mill scale) |
Smoother, brighter, scale-free |
| Mechanical Properties |
Lower strength and hardness, higher ductility |
Higher strength and hardness, better machinability |
| Final Thickness |
Suitable for producing thick sections |
Suitable for producing thinner sections |
| Production Cost |
Usually lower |
Usually higher (due to finishing processes) |






